Now we are used to the fact that the term ‘bot farm’ implies an organised group of people sending payroll messages, so-called ‘beneficial’ for the customer, and posting them on the Web from purposely formed accounts. Moreover, we are used to scandals involving the application of such tools for political campaigns and the competition of business giants.
It is worth reminding of certain Russian Internet research agencies, nicknamed in the media as a ‘troll factory’, ‘The Prigorin trolls’, ‘Olgin trolls’, ‘Kreml-bots’, etc.; the agencies that are actively engaged in disinformation and the public opinion shaping through social networks, on-line publications, thematic sites, profile resources by means of fake accounts just to advance the positions of customers and meet their targets.
According to the investigation data, the above-mentioned agencies were involved in the Eastern Ukraine military conflict and the civil war in Syria. In addition, currently these agencies have been charged on the evidence of the investigation conducted by the American Prosecutor Robert Muller, according to which Russian Internet research agencies were identified as interfering in the U.S. presidential election in 2016, as well as fuelling intra-national conflicts. In 2018, criminal charges were brought in the USA against the organisation and its leaders in absentia. Furthermore, the organisation associates, as well as the agency were included on the US sanctions list.
The so-called astroturfing (the public opinion manipulation) is also used in the commercial field. For instance, in 2001 Microsoft sponsored the Americans for Technology Leadership movement, which started a mass legal action in the United States in order to protect the corporation against antitrust lawsuits and create a visible public endorsement of it.
In 2007, the search engine Ask.com launched an advertising campaign against the Google search system, which it represented as a monopolist liable to harass the Internet. In 2010, the activities of Reverb Communications were exposed, hiring trainees to post positive reviews of some games on the iTunes Store. In 2017, Fidelity Communications, an internet service provider from the American state of Missouri, financed an anti-expansion initiative to increase municipal broadband connectivity. This was revealed by a YouTube user who found the provider’s name on the initiative website file titles. The company then admitted to funding the initiative.
So why now, in the Coronavirus era, the campaign period in the United States, Ukraine and a number of European countries, has something like a ‘Bot farm’ vanished from the front pages, for some reason? Has it ceased to exist? SEO Professional Jim Jameson used to work for Americans for Technology Leadership and supplied the insider data to our editorial board.
Jim, why is it that we are not seeing anything happen today about ‘Bot farms’? “Over the last five years, the ‘Bot farms’ phenomenon has undergone a considerable transformation. The point of this dramatic development is as follows: the owners changed their approach to marketing policy greatly. Previously, Bot farms were treated as a business, rather profitable one, different customers were involved in it successfully. Hence, 200-400 people office group could serve a variety of flows and different tasks. To claim, the owners are acting alternatively today or the marketing s being transformed means that these structures are simply closed. In fact, there is only one owner who produces this kind of structure, doing this for himself, so the entity serves solely one client”.
In the movie “The Godfather”, for instance, Tom Hagen was a head lawyer of Corleone family thus having a single client, Mr. Corleone. Just in the same way that the Bot farm has a single client these days. And this client is the maker or the creator of this Bot farm.
However, wouldn’t that ‘Bot farm organisation procedure’ require a lot of money? “It is a rather grand myth today that one needs to own factories or huge business corporations just to create a Bot farm. Well, once it was a novelty, it was definitely expensive; maintenance, safety and technical implementation required huge money. But since most of the stuff is being replicated and distributed around the world, everything eventually gets optimised. People discover new techniques, approaches, ideas and methods for upgrading such technology and making it more and more available, even for a mid-sized company in Europe, whose business structure itself numbers 50 and 100 people approximately, for example. Before, this was almost impossible, in fact, today it is a reality. Every structure may use its own Bot farm, no-one is aware of. Moreover, lots of marketing issues are implemented through the Bot farm resources.”
«…a particular partnership system is arising as one Bot farm is insufficient to provide access to… let me say, the thirty media sites in many different countries and on different continents».
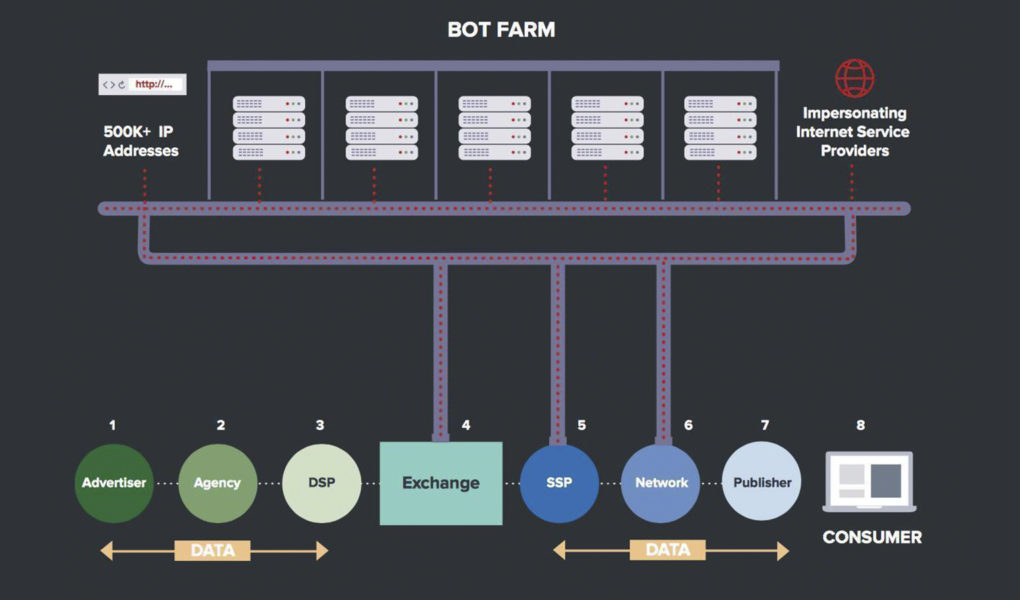
What developments have occurred to the Bot farms and what caused them? “The configuration of this Bot farm’s tools has changed, i.e. in the classic representation the bot farm referred to activities involving creating communities on social networks, commenting on Reddit, YouTube, Facebook and other socials, in essence, managing some kind of feedback. Therefore, no matter how brilliant the article is, if the comments say ‘it’s all bullshit’, many readers will believe it really is. This has had a significant impact and still influences the perception of the product, the individual, the company and so on”.
Well, today the old methods of the Bot farm can no longer be used, that’s not sufficient at all. The list of technical arsenal or tools should be significantly expanded. Unlike previous steps, today one requires more than mere bots and the so-called SMM Specialists, i.e., the SEO Specialists. We are going to refer to bots as operators that monitor the information space for 16-18 hours a day and operate from 20 or 100 different accounts simultaneously. Nowadays, technical capabilities make it possible to provide this. However, apart from that, one also needs other tools today, for example, a private media or some other resources very similar to media. Essentially, there is a sort of partnership system emerging simply because one bot farm is no longer sufficient to provide access to, for instance, 30 media from different countries and different continents. Certainly it is acceptable to pay some media for the publications, still the budgets meeting that journalistic purpose are too huge; that sounds like a completely irrational waste of money. One more thing, it is not safe to use someone else’s resources. For this reason, some ‘networks’ have developed, which already include tens of thousands of websites.
These ‘nets’ were produced in pieces, some by European groups, some by Americans. There exist coordinators for these ‘networks’, as nets are a commercial product themselves, so they have to be monetised. Accordingly, the bot farm must be connected to the ‘networks’, since bot farm may function, to some extent, re-directing those resources, which may include the media, thematic sites and profile ones, to solve the tasks.
This means that the current or present-day generation of Bot farms structure consists of the following:
- Coordinators serving the media networks;
- A group of journalists who write ‘what is required’ and post such articles and/or some other products on partner networks resources;
- Technicians;
- And finally, the bots that do not just use ‘comments and/or shared opinions and special tags anymore, but also refer to some counter-views resources or web-sites publishing entries and articles, etc. thus achieving the initial marketing goals.
«…that’s how a loop or cycle is shaped»…
What brings to the forefront today? “The lack of groups of specialists who work on Wikipedia is obvious (I mean the experts modifying certain materials on Wikipedia). At the same time journalists, bot operators and others are also a great necessity. For instance, the journalists publish some new articles in the affiliate media networks, afterwards this data and links are being cited on Wikipedia. I mean, this makes it possible to modify and re-write any Wikipedia entry. So far, the bots are getting even more powerful tools to use, since the bots ‘write \ re-write \ duplicate data’, referring to different media that are not connected to each other, at the very first glance. The new resources and artificially created media mass allows one to interfere with Wikipedia entries’ contents, since there is huge bunch of links and proper media exposing ‘new data’ to refer to as an authoritative and credible one. This scheme is all about re-creating anything on the Web for relevant purposes.”
For instance, some news was deliberately released that made it even possible in the Turkish Wikipedia to call Recep Erdogan, the president of Turkey, a tyrant. The media reports such news and all readers think that the tyrant is now a logical reason. No one notices, however, that before this precedent, another network of ‘not-so-credible media’ was generated on advance; it spread the word ‘tyrant’ sticking to Erdogan. On that basis, Wikipedia’s entry dedicated to President Recep Erdogan changed, and after that the ‘news about the tyrant’ was published by the central American media with reference to Wikipedia. This is how a vicious cycle is generated, and in the loop the bot farm may discreetly starts to control the opinions of authoritative media and use them to someone’s benefit.
Summing up
In a strongly competitive marketplace environment, we are constantly witnessing the market tools change, and one requires that knowledge to achieve success. Things that used to work yesterday may lose their effectiveness today. The most important factor for success in defending and retaining one’s position is how rapidly one can anticipate and adjust to changes. And if you are willing to survive on the market today, you just have to create a similar structure that will protect your interests from competing structures, on the one hand, and effectively implement your marketing policy, on the other hand.